The influence of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau (TP) on atmospheric heat source (AHS) is one of the important factors affecting Asian summer monsoon precipitation. A deep understanding of the relationship between the snow cover and AHS over the TP can help to improve the predictions of the Asian summer monsoon. Funded by “The interaction of climate system in the three poles on earth”, group of Prof. Anmin Duan explored the relationship between the plateau snow in late spring and AHS using the WRF model and reanalysis data.
They found that only a weak negative relationship exists between snow depth and the AHS over the western TP and the weak negative atmospheric heat sink was only detected by the ERA-Interim reanalysis at a grid spacing of 0.75o×0.75 o(Figure 1b). However, the WRF model, driven by satellite snow data, shows a strong atmospheric heat sink over the western TP and the Nyenchen Tanglha Mountains, where the altitude is above 4,000 m with thick snow cover. The AHS can be decomposed by five parts in WRF, i.e. the cumulus scheme (CU), microphysics scheme (MP), longwave radiation scheme (LW), shortwave radiation scheme (SW), and planetary boundary layer scheme (BL).Results show that the underestimated atmospheric net long wave radiative cooling effect which is associated with snow depth may exaggerate the AHS in current reanalysis data sets.
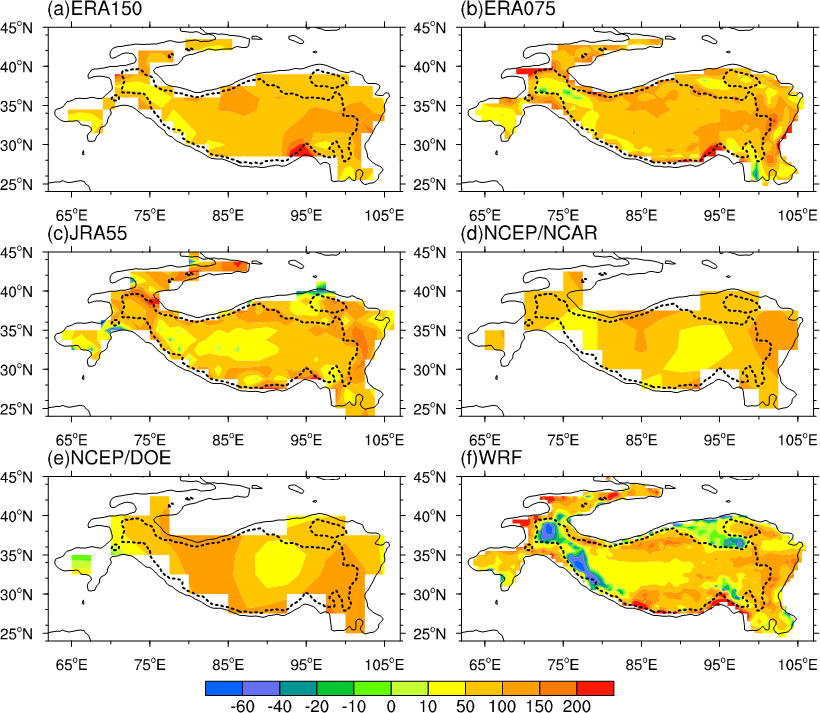
Figure 1 Spatial distributions of the AHS (units: W/m2) in May, averaged over 2011–2016, derived from (a) ERA150, (b) ERA075,(c) JRA-55, (d) NCEP/NCAR, (e) NCEP/DOE, and (f) WRF. Black solid linesand dashed curved lines outline the areas of the TP with an average altitude greater than 2000 and 4,000 m, respectively.
Reference: Xiao, Z. X., A. M. Duan*, Z. Q. Wang. 2019: Atmospheric heat sinks over the western Tibetan Plateau associated with snow depth in late spring. International Journal of Climatology, 39(13), 5170-5180. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6133.

