Recently, the study team of Prof.Guo Huadong, who is responsible for CASEarth, has produced a multi-phase product of urban and rural construction land in China with the Big Earth Data processing platform and machine learning technology, revealing the characteristics of the sprawl of provincial capitals in China.
With the development of global urbanization process, a large number of people from rural areas continue to flood into cities, thus the scale of urban construction land continues to increase. At present, about 50% of global population, i.e. 3.5 billion people, are living in cities. This number is expected to grow to 5 billion by 2030. Besides, 95% of urban sprawl will occur in developing countries. Urban sprawl refers to a land development phenomenon characterized by low density, imbalance and extensiveness in the process of rapid urban development. It may impose many negative effects on economy, society, ecology and environment, etc. Grasping the pattern and trend of urban sprawl is crucial for the implementation of the UN’s sustainable development goals (SDGs) and new urbanization strategies in the context of urbanization in China.
This study automatically produced a six-phase product of urban and rural construction land in mainland China from 1990 to 2015 based on the remote sensing satellite image data and the Big Earth Data processing platform, in combination with the image spectrum, texture and morphological features and by means of the machine learning technology. It is verified that the overall accuracy of the product is above 90%. On the basis of this product and in combination with demographic data, quantitative comparison and analysis of the speed, degree and pattern of the urban sprawl of provincial capitals in China were carried out.
This study found that provincial capitals in China show the trend of overall urban sprawl and that land urbanization is obviously faster than population urbanization. From 1990 to 2015, the annual growth rate of population in provincial capitals was 2.31%, while that of urban construction land was 5.16%. The latter was 2.42 times of the former. Most of (26) the provincial capitals studied experienced urban sprawl. Cities with a high degree of urban sprawl (urban sprawl index > 7) include Nanjing, Chongqing, Wuhan and Hangzhou. Therefore, in the process of urban development and construction, powerful measures should be taken to improve the utilization efficiency of land resources, reasonably control the trend of the urban sprawl of provincial capitals in China and promote the sustainable development of cities.
This study was funded by the Digital Belt and Road Research Project, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Key Research & Development Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
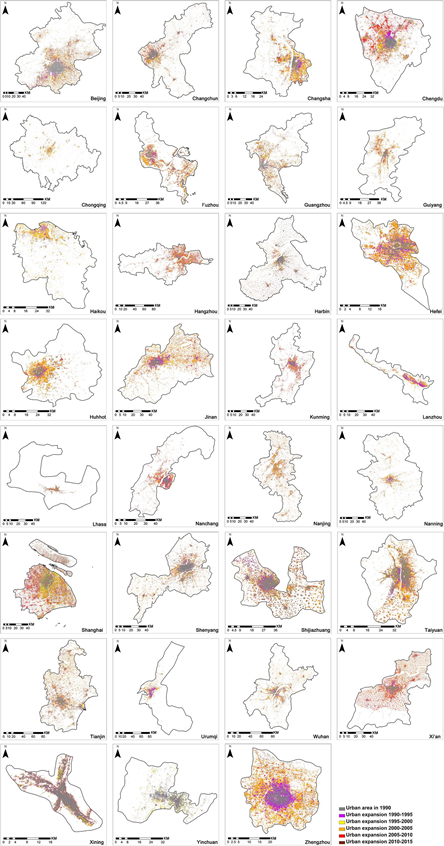
Spatial Expansion Diagram of Provincial Capitals in China (1990-2015)
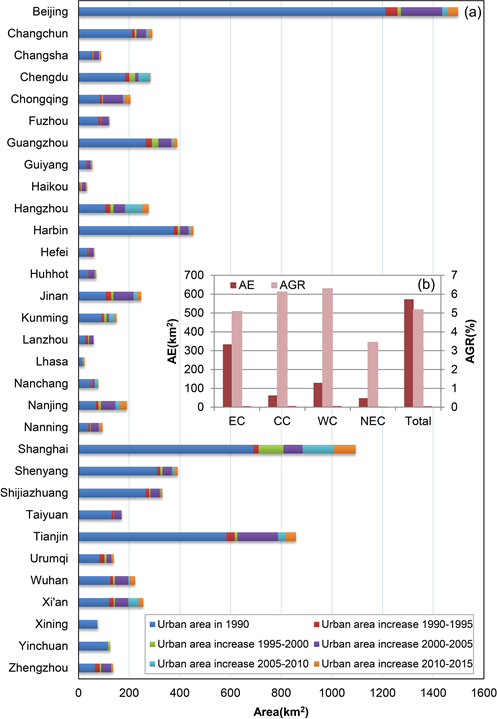
Statistics on Growth of Construction Land in Provincial Capitals in China (1990-2015)
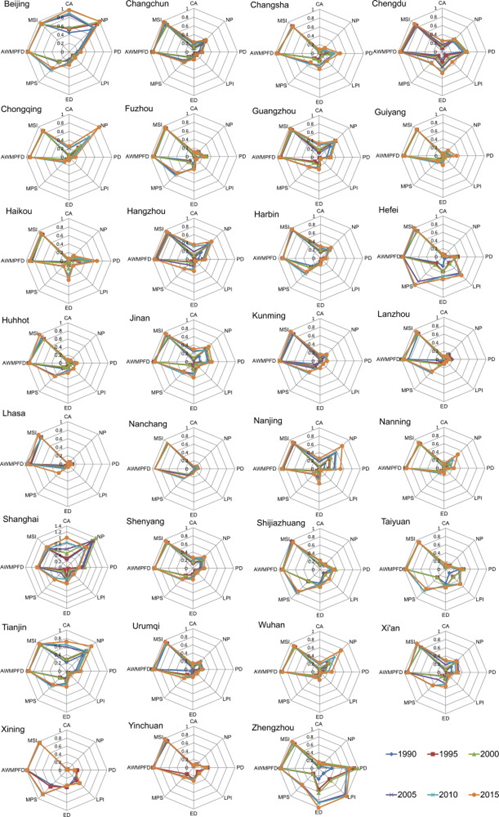
Statistics on Landscape Parameters of Provincial Capitals in China (1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2015)
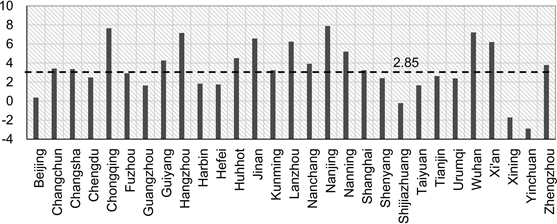
Statistics on Urban Sprawl Index of Provincial Capitals in China

